Goo is an open and collaborative project started in Sean Megason's group at Harvard University. We welcome everyone who is interested in enhancing 3D models of biological cells with Blender. The developer’s guide is to help contributors willing to start working and contributing on Goo. If you are interested in join, please contact Sean Megason - sean_megason AT hms harvard edu.
The first thing you need to do is to fork the Goo repository and then clone the forked repository into your local machine. This will give you the freedom to test and make changes to the project without affecting the original repository.
Make sure you have git installed on your local machine. If you do not have it install on your system, refer to this guide.
Fork & clone
If you are new to Git/Github, refer to this guide to learn how to fork and clone a repository from Github:
Push
Once you make final changes and the scripts run with no issues, you can push them into the main project. This guide instruction on how to add, commit and push using git.
Blender is an amazing open-source and free 3D computer graphics software, widely used in motion design, graphism, animation, and becoming increasingly popular in sciences. Its Python API comes handy for developers willing to extend Blender’s capabilities, much like Goo does. Blender has a huge community and contributors all over the world, which gathers every year at Blender convention and every day on the Blender community discord.
Once you have downloaded and installed Blender, launch Blender and select General to open a new file. The scripting tab allows you to interact with Blender using Python. By clicking scripting, a list of windows will open:
3D Viewport allows you to interact with 3D objects.Python Interactive Console allows you to interact with Blender using Python language.Info Console Menu or Report console creates a log in Python of the executed actions on Blender. In another words, it translates the clicks you made in Blender into code. This is very useful especially when you try to automate procedures of actions on scripting.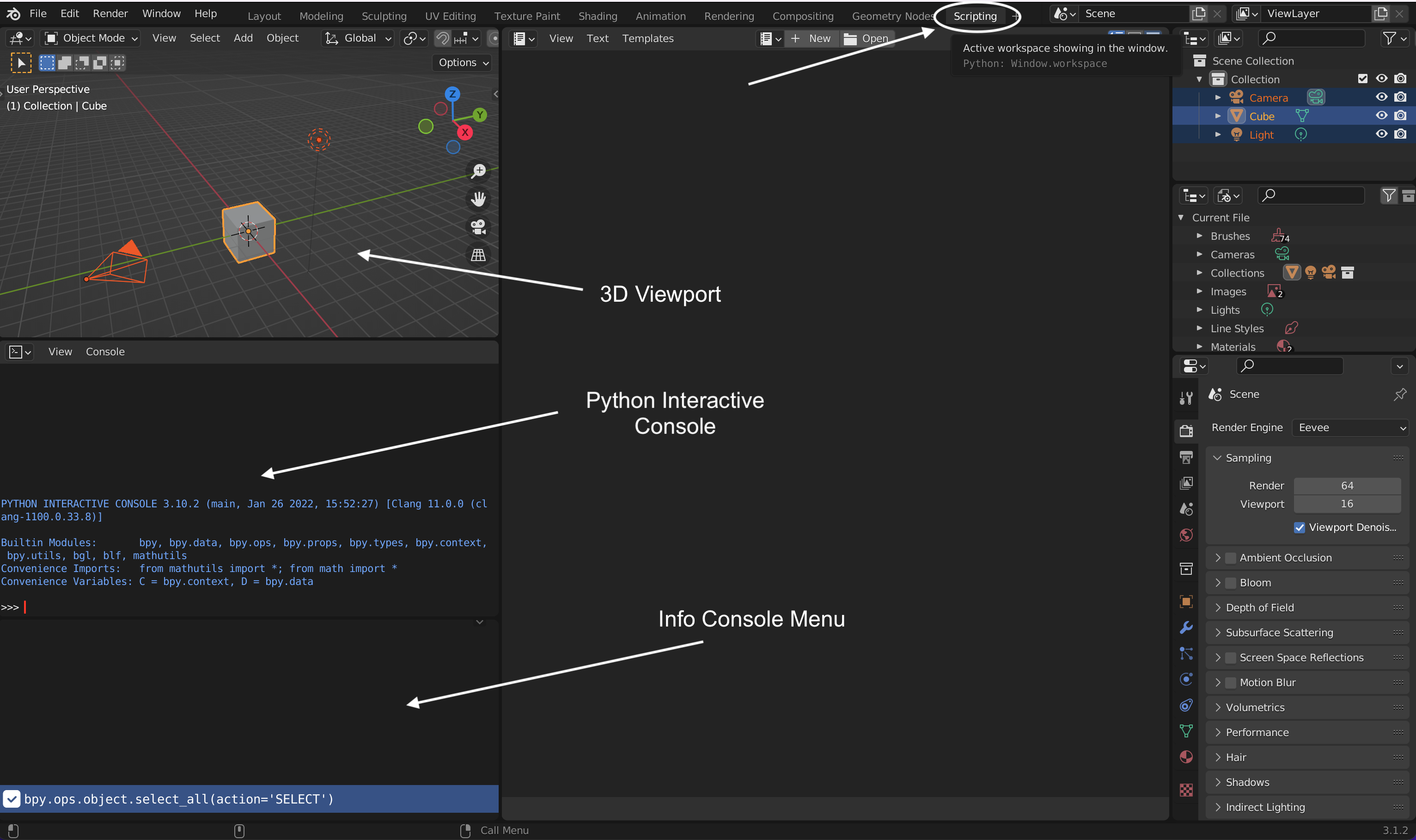 |
| Blender’s scripting environment |
Creating Python File
You can create a Python file and run it on Blender. Once you are in Scripting tab, click on the + New icon.
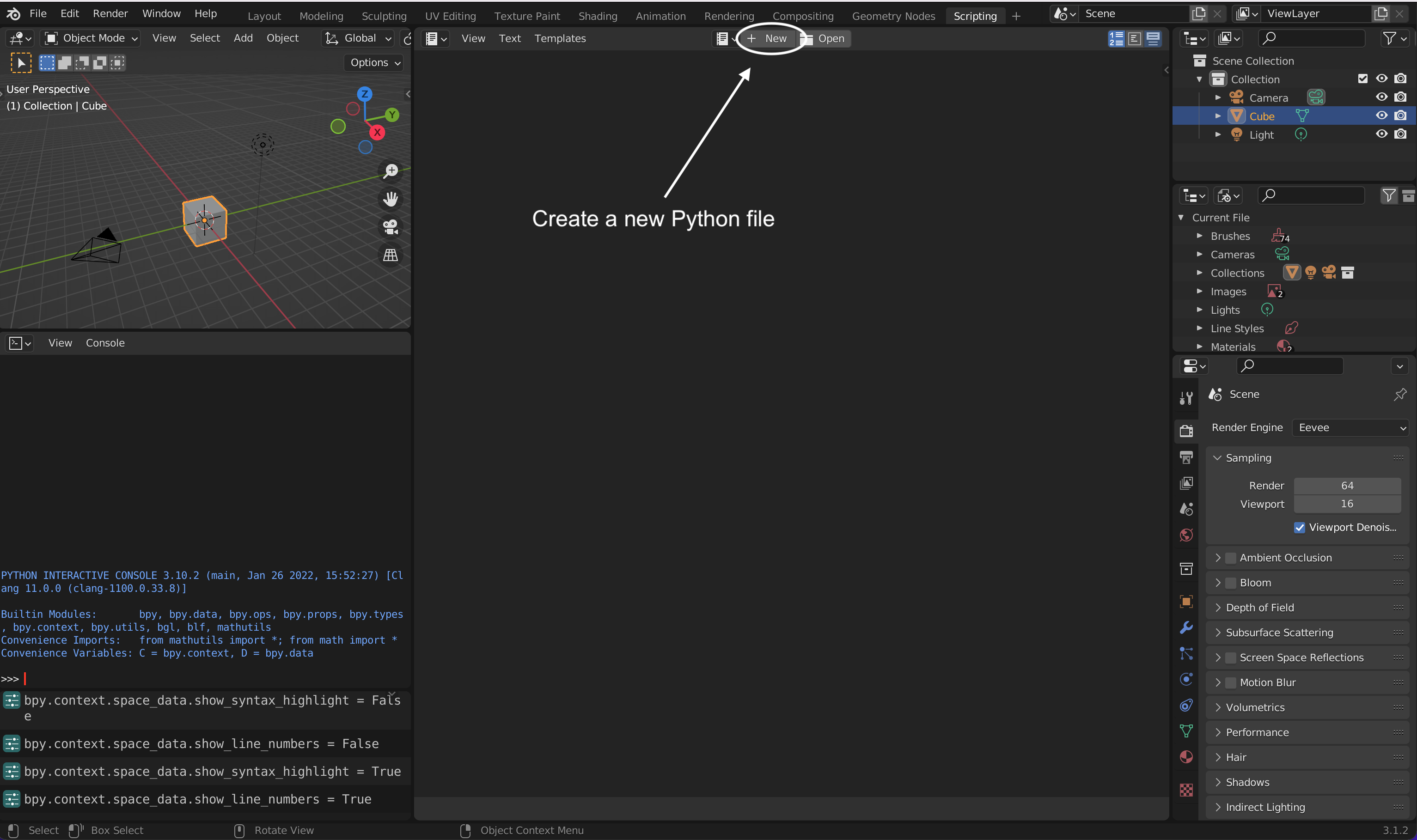 |
| Open a python file in Blender’s scripting environment |
Blender Python’s API, named bpy, allows Python and Blender to fit together. To use it, the following package should be imported:
import bpy
The Blender API can used with no installation nor importing into the Python Interactive Console. The Python file can be run on Blender by clicking on play icon.
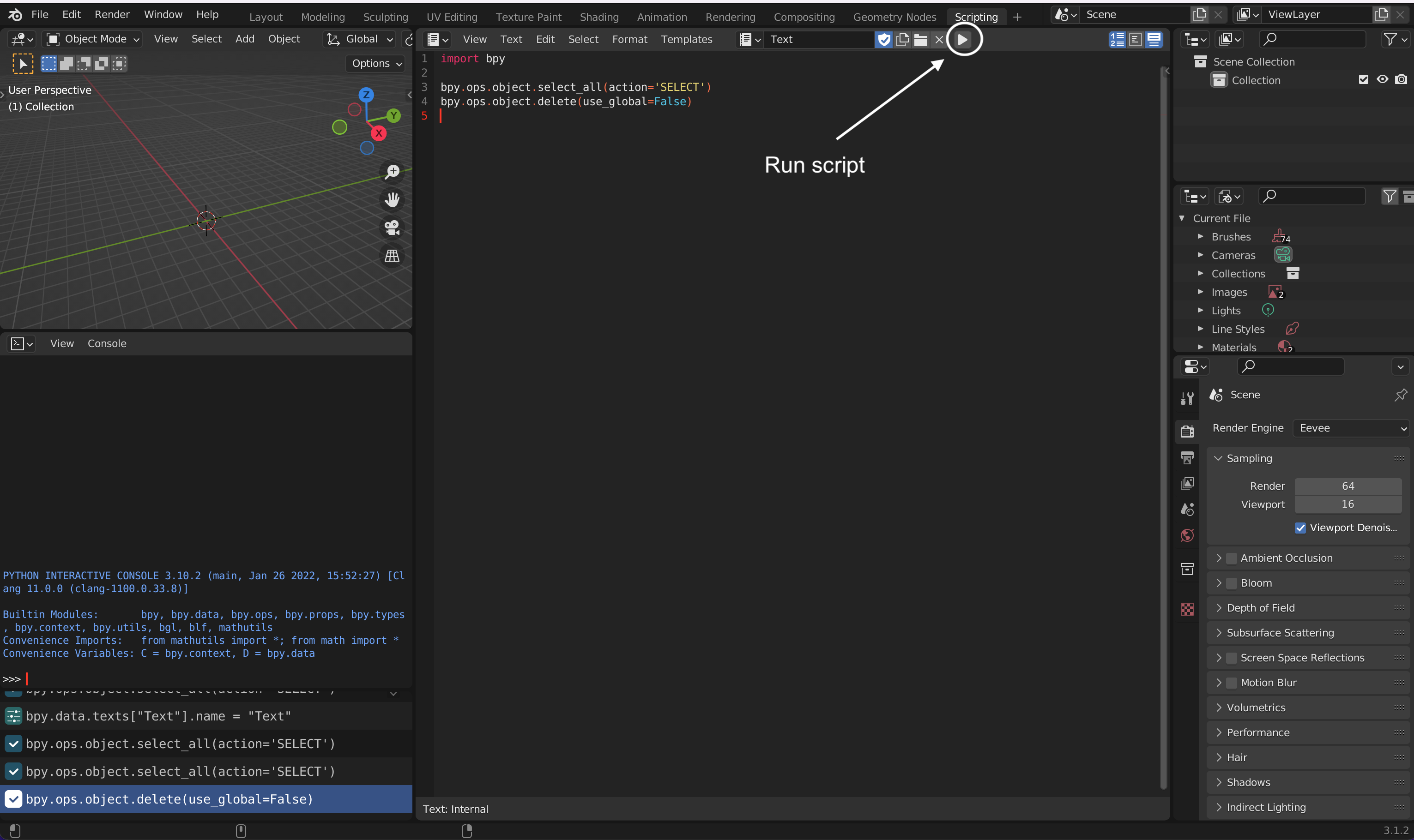 |
| Run a script from Blender’s scripting environment |
Viewing Python Error Messages
Window > Toggle System ConsoleFinder > Applications > Right-click on Blender > Show Package Content > Contents > MacOS > Right-click on Blender > Make Alias. Blender will be launched by double-clicking the Blender alias and any error messages will display on the alias window. You can store the alia in any folder.Blender Python Tutorials
You can find many free tutorials on YouTube and the Internet. here is a great tutorial, made by Darkfall, on YouTube on how to write a Python script in Blender.
Useful Blender Tips
View and mark the checkbox of Line Numbers. View tab will appear once you create a Python file.View and mark the checkbox of Highlight Line. View tab will appear once you create a Python file.Developer Extras, go to Edit > Preferences > Interface > Check Developer Extras.Python Tooltips, go to Edit > Preferences > Interface > Check Python Tooltips.You can use any IDE softwares (Atom, PyCharm, Anaconda,…etc) available on the internet, but from our experience Visual Studio Code has been very smooth and convenient to use.
Getting started with VSCode:
python –version on Terminal/Command Window. If it returns python with some numbers, then you know Python already was installed. But if it does not, you need install Python.pip install fake-bpy-module-latest. This command line will install the latest Blender’s version available using Pip package manager. For more info on visit Fake Blender Github.File > Open Folder. See Git/GitHub section on how to clone Goo on your local machine if you have not done it yet.Terminal tab and then select New Terminal.ctl + shift + P and type Python: Enable/Disable Linting. Click on it and enable it. Now you need to select the code style. Again click ctl + shift + P and type Python: Select Linter and then select flake8.We have already shown how to run Python codes in Blender (see Creating Python file above). In this section, we will show you how to run Python scripts on VSCode written exclusively for Blender.
Recommended: developing Python scripts in VSCode and executing in Blender
from importlib import reload
reload(goo)
Alternative: developing/Executing Python codes in VSCode
Blender Development by Jacques Lucke.Ctl + Shift + P , select Blender: Start, and then select the executable Blender (you can find it in Blender folder). With MacOS: Finder > Application > Right-click on Blender and choose Show Package Content > Contents > MacOS. With Windows: find the path where blender.exe exists in Blender folder. Once you link the executable, Blender will launch. Select General to start from scratch.Ctl + shift + P and select Blender: Run Script. Now, you can see the results in Blender.